Keys in flutter.
What are the keys?
A key is an identifier that allows you to uniquely identify and differentiate between widgets.
Wanna watch video instead.
Types of Keys
- ValueKey: This key is used when it has to be assigned to something constant and extraordinary. It is generally used in a list of children where the value of every child is different and constant.
itemCount: tasks.length, itemBuilder: (context, index) { final task = tasks[index]; return TaskItem( key: ValueKey(task), // Using ValueKey with task as a unique identifier taskName: task, onTaskCompleted: () { _markTaskCompleted(index); }, ); }, )
In this example, we have a list of tasks. Each task is assigned a unique ValueKey based on its value. Since Value is unique.
- ObjectKey: The Object key is used when any single field such as name or birthday, they may be the same for more than two. It is the same as the Value key with the only difference being that it takes in a class object that holds data.
ListView.builder( itemCount: users.length, itemBuilder: (context, index) { final user = users[index]; return UserItem( key: ObjectKey(user), // Using ObjectKey with user as a unique identifier userName: user.name, ); }, )
In this example, we have a list of users. Each user is assigned a unique ObjectKey based on the user object.
- UniqueKey: The unique key is used when you need a key that is unique across the entire app.
class MyWidget extends StatefulWidget { MyWidget({Key? key}) : super(key: key ?? UniqueKey()); @override _MyWidgetState createState() => _MyWidgetState(); }
When to Use Keys
If you find yourself altering (e.g., adding, removing, reordering) a list of widgets of the same type that hold state, chances are high you need any type of key. Keys should be used with particular widgets such as ListView and some stateful widgets that need to maintain their state across page navigations. ExampleHere is an example of how keys can be used in a Flutter application:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MaterialApp(
home: MyApp(),
));
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Flutter Keys Example'),
),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: 10,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
return ListTile(
key: ValueKey(index),
title: Text('Item $index'),
);
},
),
);
}
}
In this code, we have created a ListView with 10 ListTiles. Each ListTile is assigned a unique ValueKey based on its index in the list.
Where do I put ‘em?
Short answer: if you need to add keys to your app, you should add them at the top of the widget subtree with the state you need to preserve.
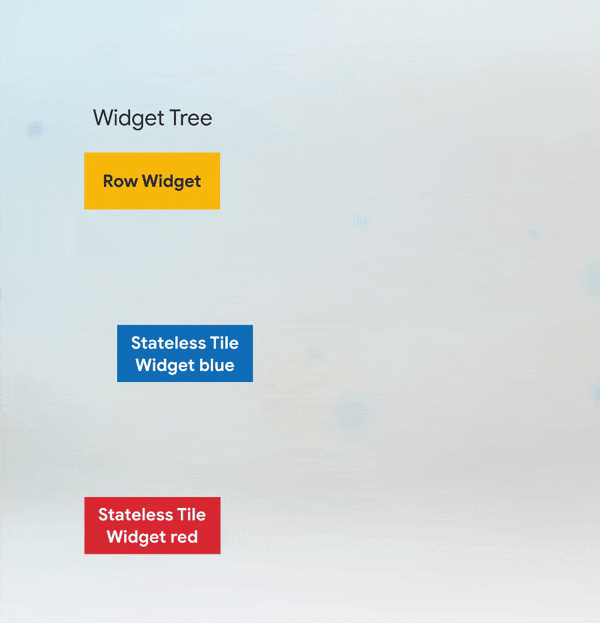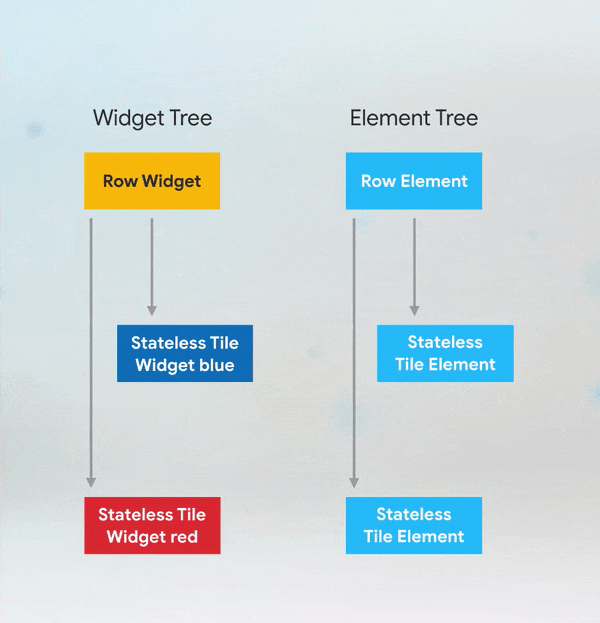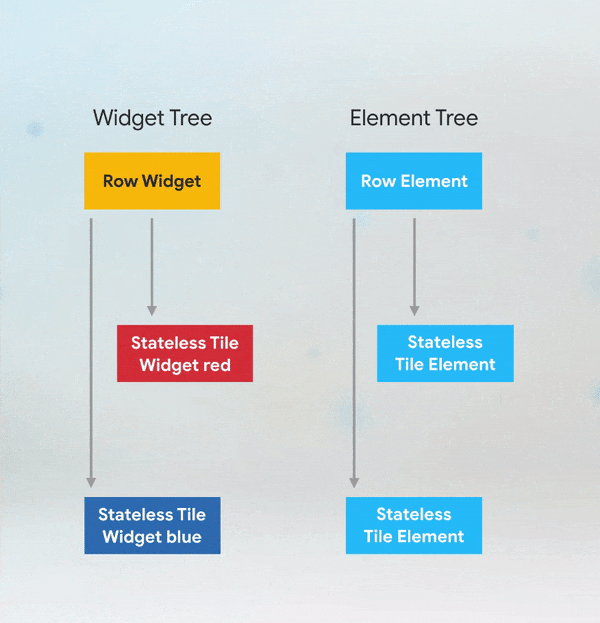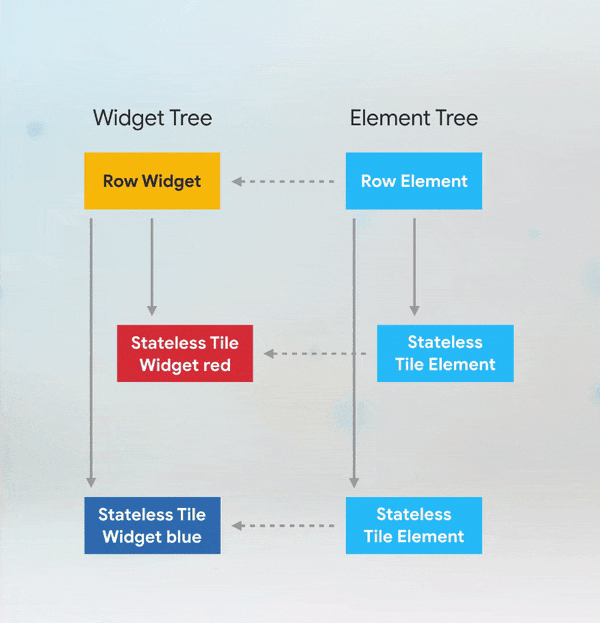
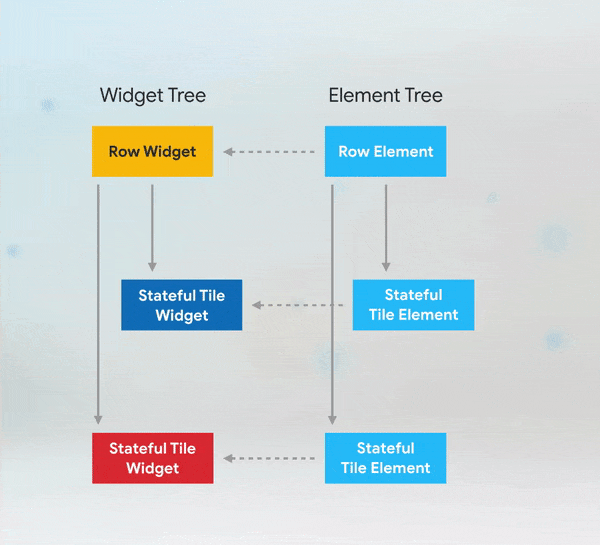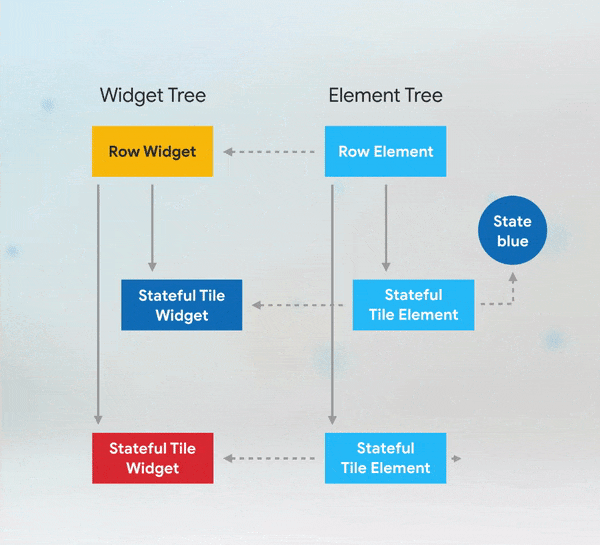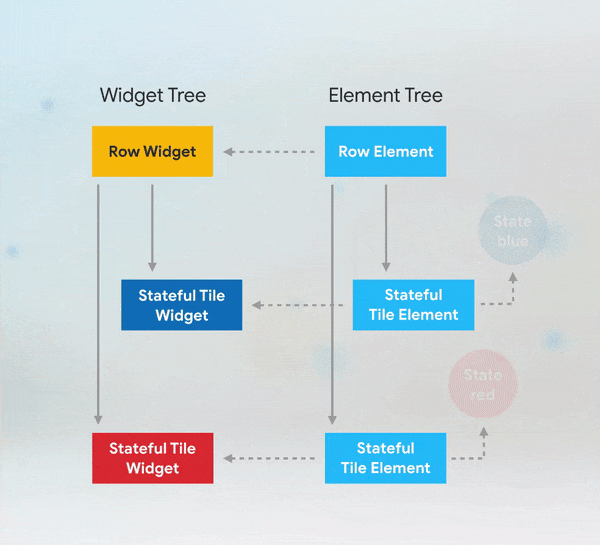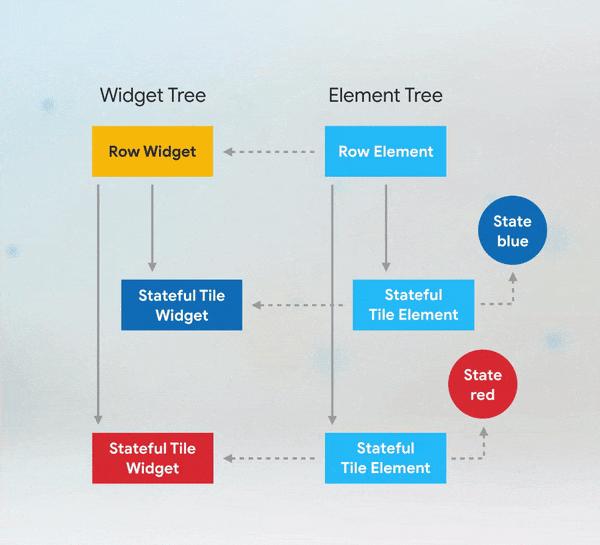
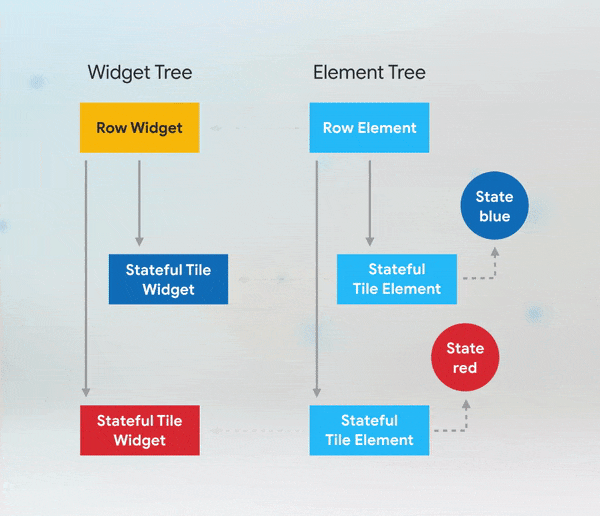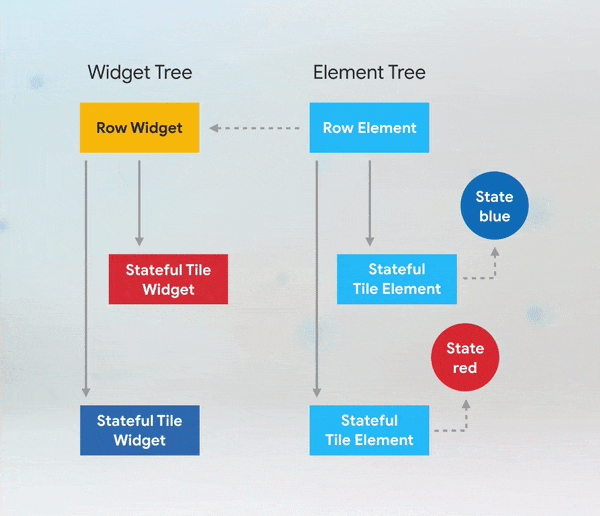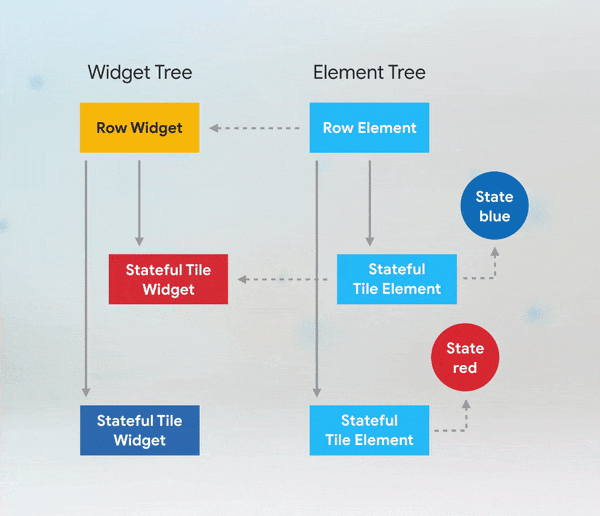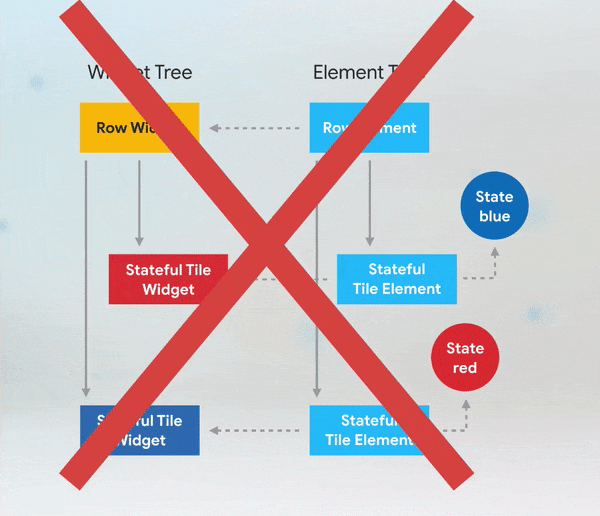
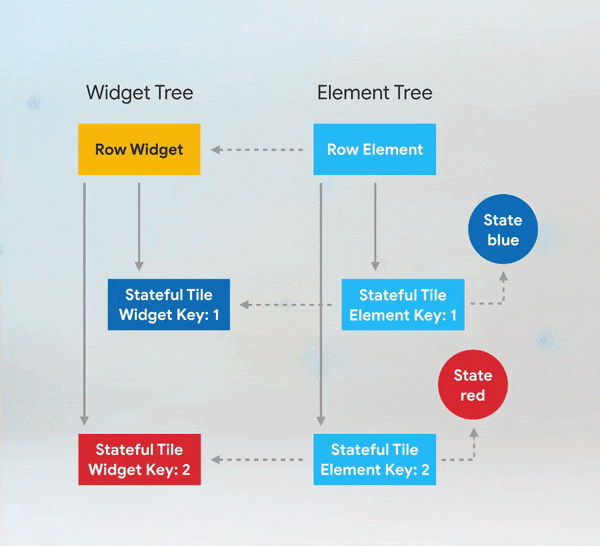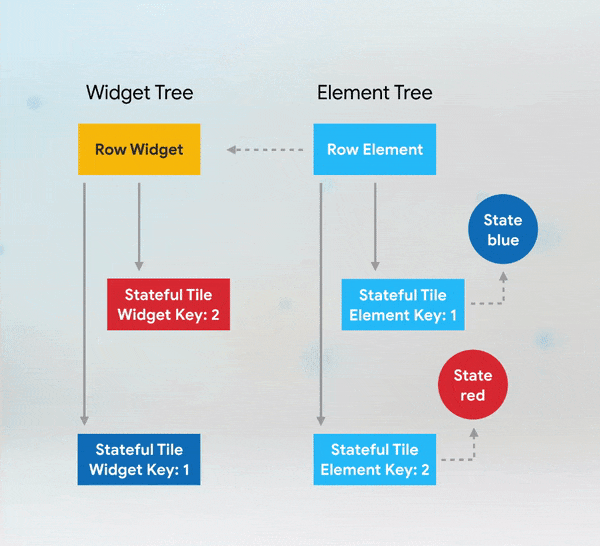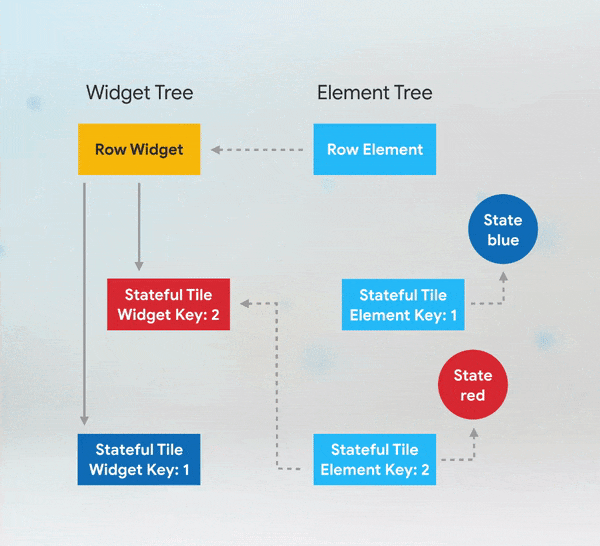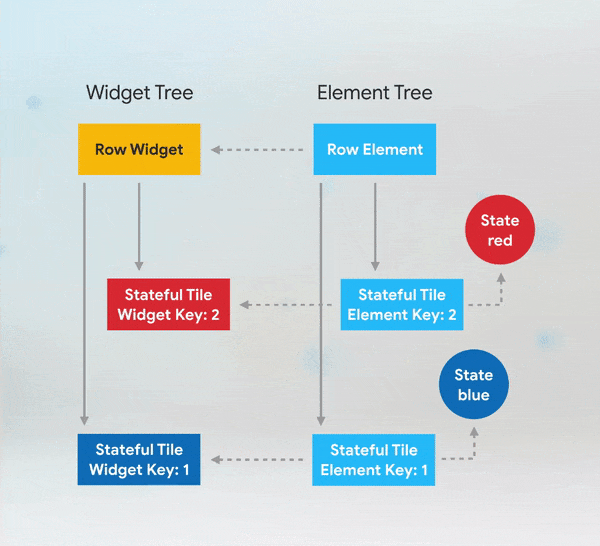
More Details: keys flutter builder vs keys flutter widget valuekey or key Alternatives to KeysWhile keys are useful in many scenarios, there are alternatives depending on the use case:
- Providers, Inherited Widgets, etc.: These can be used to access a state of another widget from anywhere in the widget tree.
- Builder: This can be used to obtain a handle to the widget tree. Remember, keys are relatively expensive, so if you don’t need any of the features listed above, consider using a Key, ValueKey, ObjectKey, or UniqueKey instead.
keys are relatively expensive, so use them judiciously. keys practicle guide I hope this tutorial helps you understand the different types of keys in Flutter, their uses, and alternatives. Happy coding! 🚀
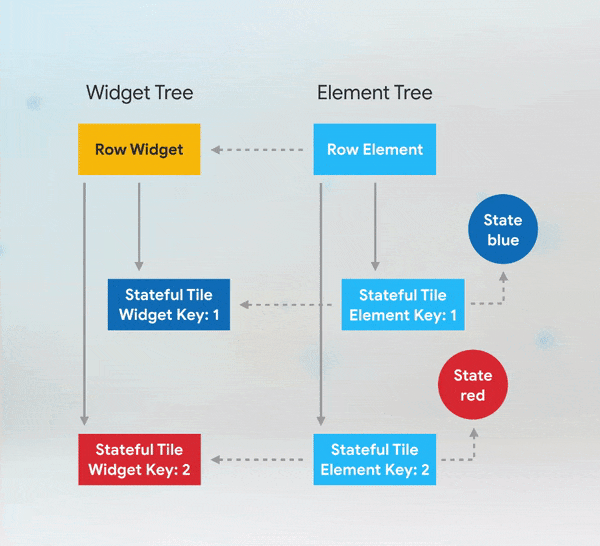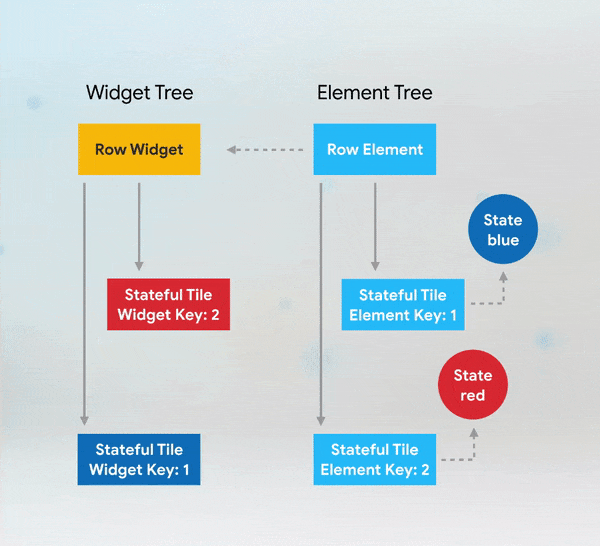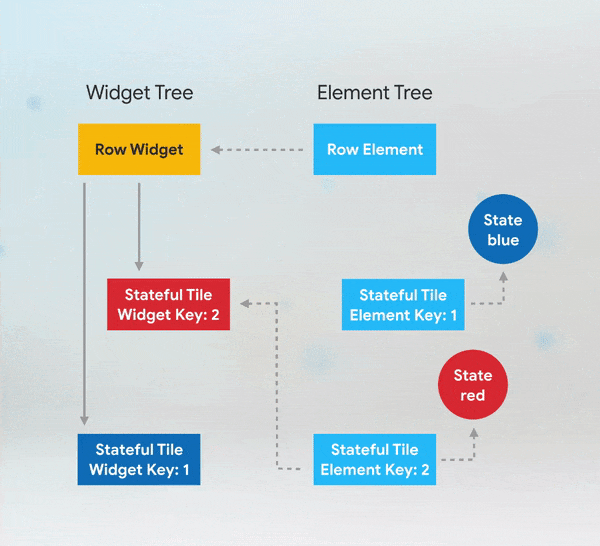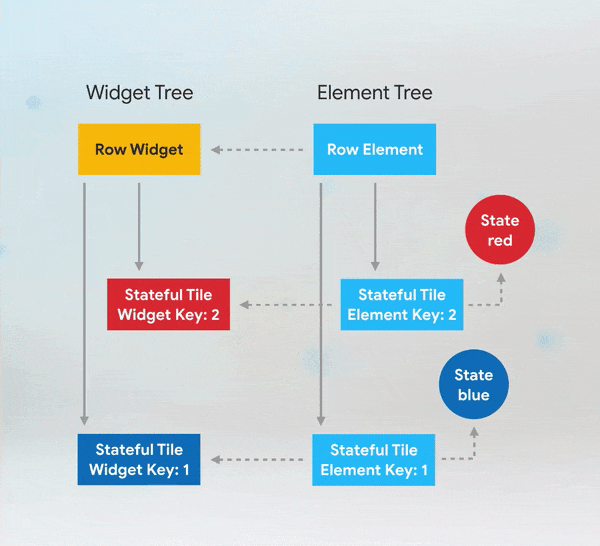
 Simple custom animation in Flutter from scratch using AnimatedBuilder
Simple custom animation in Flutter from scratch using AnimatedBuilder