Transforming Operators
Operators that transform items that are emitted by an Observable.
Buffer— periodically gather items from anObservableinto bundles and emit these bundles rather than emitting the items one at a time;FlatMap— transform the items emitted by anObservableinto Observables, then flatten the emissions from those into a singleObservable;GroupBy— divide anObservableinto a set of Observables that each emit a different group of items from the originalObservable, organized by key;Map— transform the items emitted by anObservableby applying a function to each item;Scan— apply a function to each item emitted by anObservable, sequentially, and emit each successive value;Window— periodically subdivide items from anObservableintoObservablewindows and emit these windows rather than emitting the items one at a time;
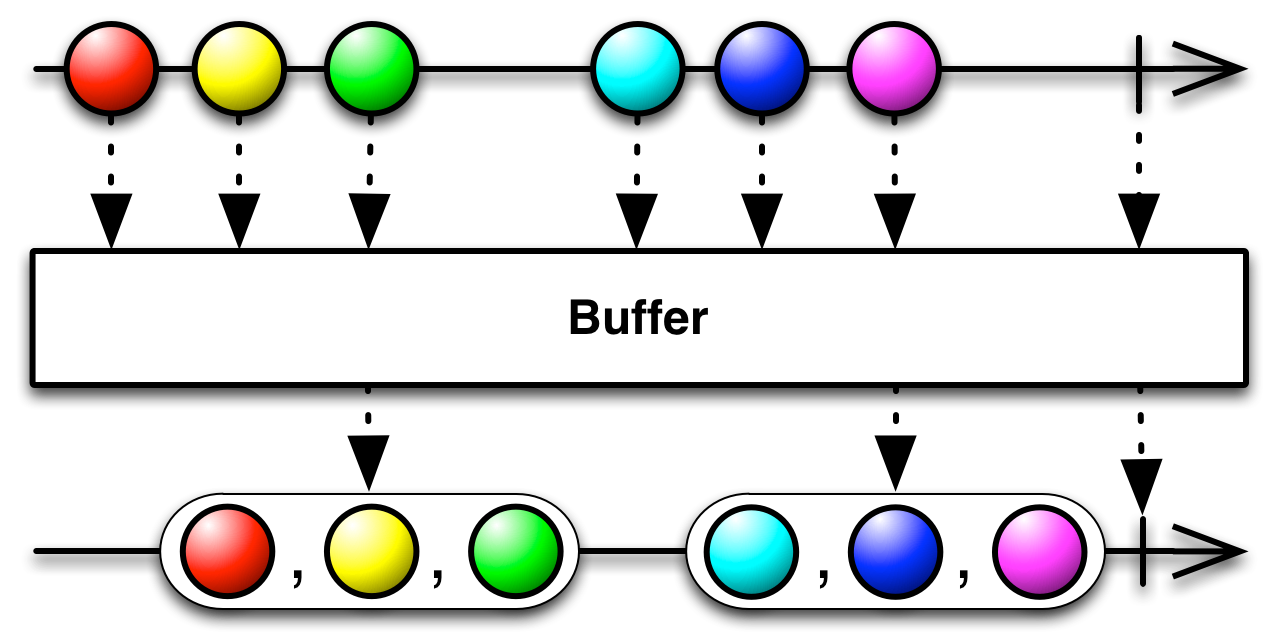
Buffer
Periodically gather items emitted by an Observable into bundles and emit these bundles rather than emitting the items one at a time. The Buffer operator transforms an Observable that emits items into an Observable that emits buffered collections of those items.
fun buffer() {
Observable.just(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8)
.buffer(2)
.subscribe { items -> println("Next item = $items") }
}
Output:
Next item = [1, 2]
Next item = [3, 4]
Next item = [5, 6]
Next item = [7, 8]
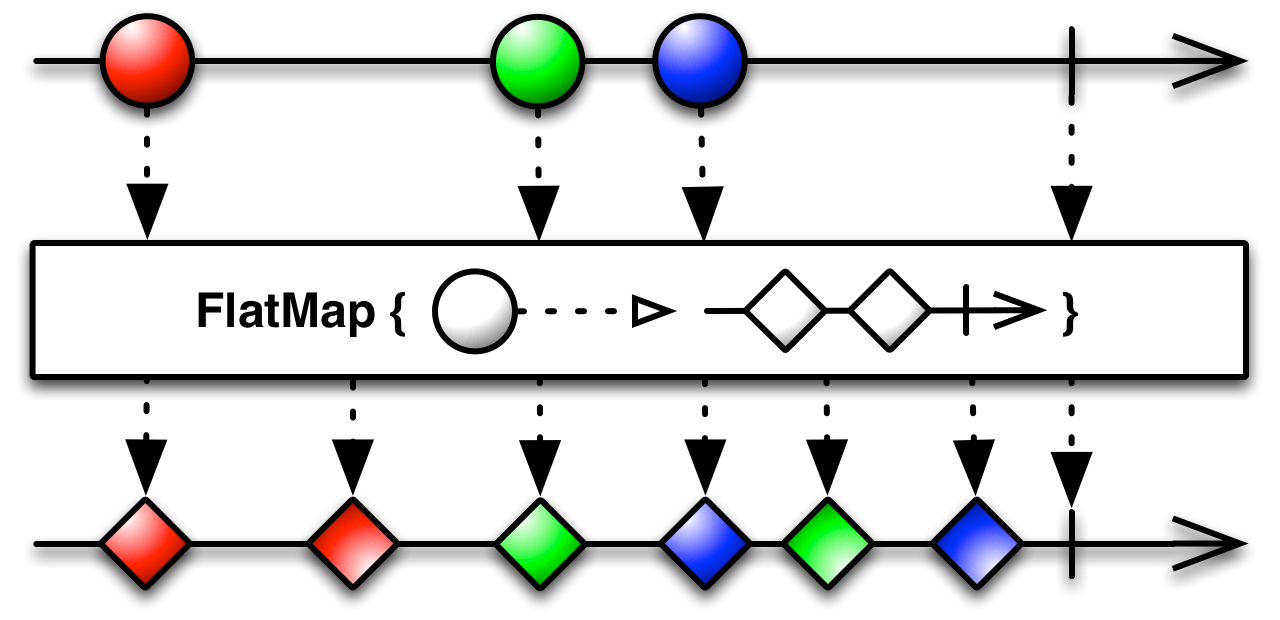
FlatMap
Transform the items emitted by an Observable into Observables, then flatten the emissions from those into a single Observable.
The FlatMap operator transforms an Observable by applying a function that you specify to each item emitted by the source Observable, where that function returns an Observable that itself emits items. FlatMap then merges the emissions of these resulting Observables, emitting these merged results as its own sequence.
This method is useful, for example, when you have an Observable that emits a series of items that themselves have Observable members or are in other ways transformable into Observables, so that you can create a new Observable that emits the complete collection of items emitted by the sub-Observables of these items.
Note that FlatMap merges the emissions of these Observables, so that they may interleave.
fun flatMap() {
Observable.just("A", "B", "C")
.flatMap { item ->
println()
Observable.just(item + "1 " + item + "2 " + item + "3")
}
.subscribe { items -> println("Next item = $items") }
}
Output:
Next item = A1 A2 A3
Next item = B1 B2 B3
Next item = C1 C2 C3
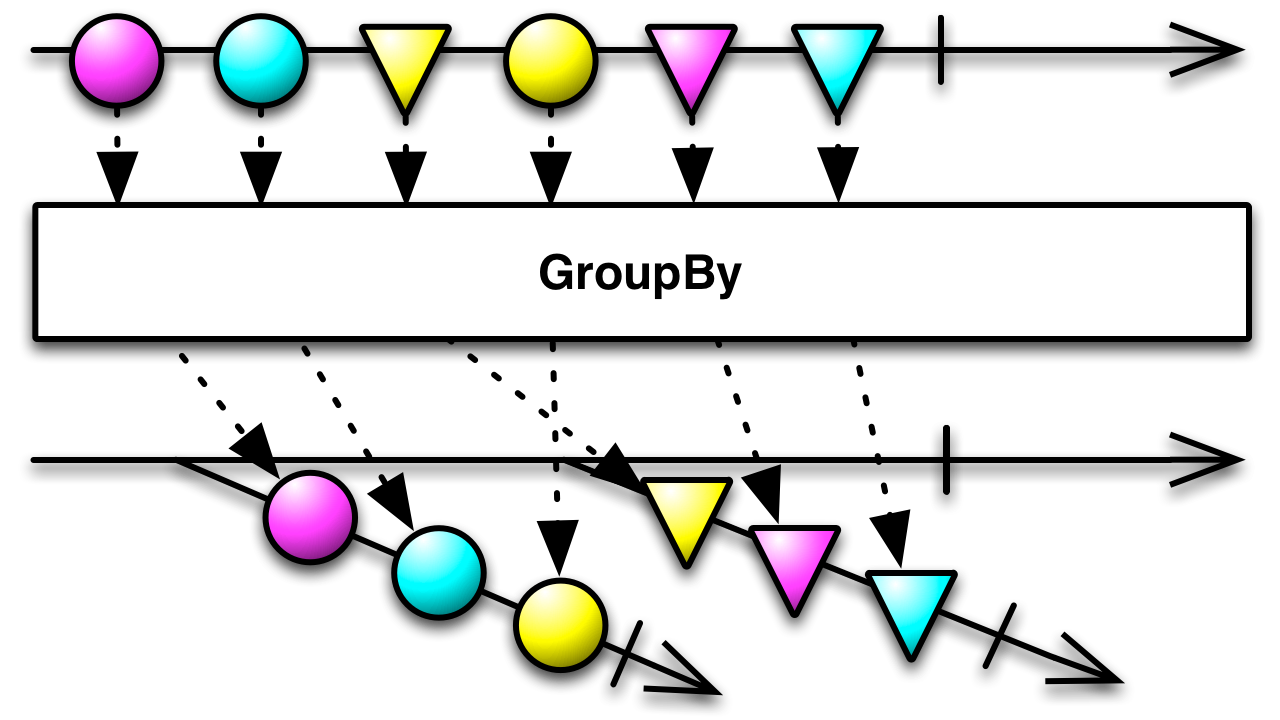
GroupBy
Divide an Observable into a set of Observables that each emit a different subset of items from the original Observable. The GroupBy operator divides an Observable that emits items into an Observable that emits Observables, each one of which emits some subset of the items from the original source Observable. Which items end up on which Observable is typically decided by a discriminating function that evaluates each item and assigns it a key. All items with the same key are emitted by the same Observable.
fun groupBy() {
Observable.range(0, 10)
.groupBy { it % 2 == 0 }
.subscribe { items ->
run {
if (items.key == true) {
items.subscribe { items -> println("Next item (key == true) = $items") }
} else {
items.subscribe { items -> println("Next item (key == false) = $items") }
}
}
}
}
Output:
Next item (key == true) = 0
Next item (key == false) = 1
Next item (key == true) = 2
Next item (key == false) = 3
Next item (key == true) = 4
Next item (key == false) = 5
Next item (key == true) = 6
Next item (key == false) = 7
Next item (key == true) = 8
Next item (key == false) = 9
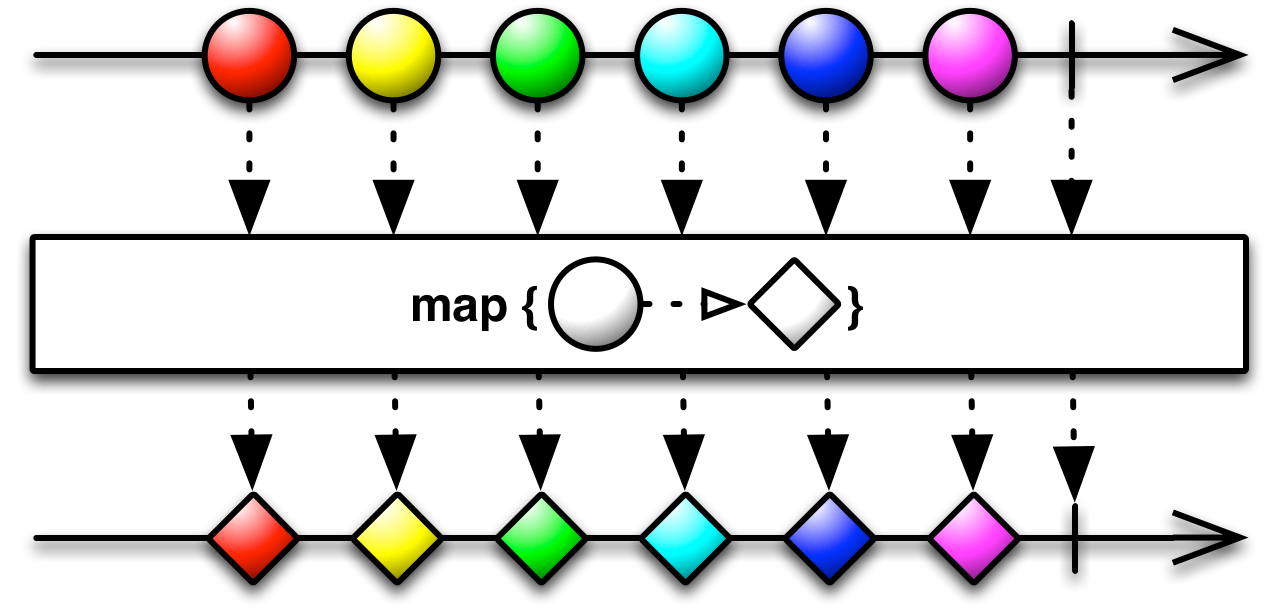
Map
Transform the items emitted by an Observable by applying a function to each item. The Map operator applies a function of your choosing to each item emitted by the source Observable, and returns an Observable that emits the results of these function applications.
fun map() {
Observable.range(0, 10)
.map { it * 2.0 }
.subscribe { items -> println("Next item = $items") }
}
Output:
Next item = 0.0
Next item = 2.0
Next item = 4.0
Next item = 6.0
Next item = 8.0
Next item = 10.0
Next item = 12.0
Next item = 14.0
Next item = 16.0
Next item = 18.0
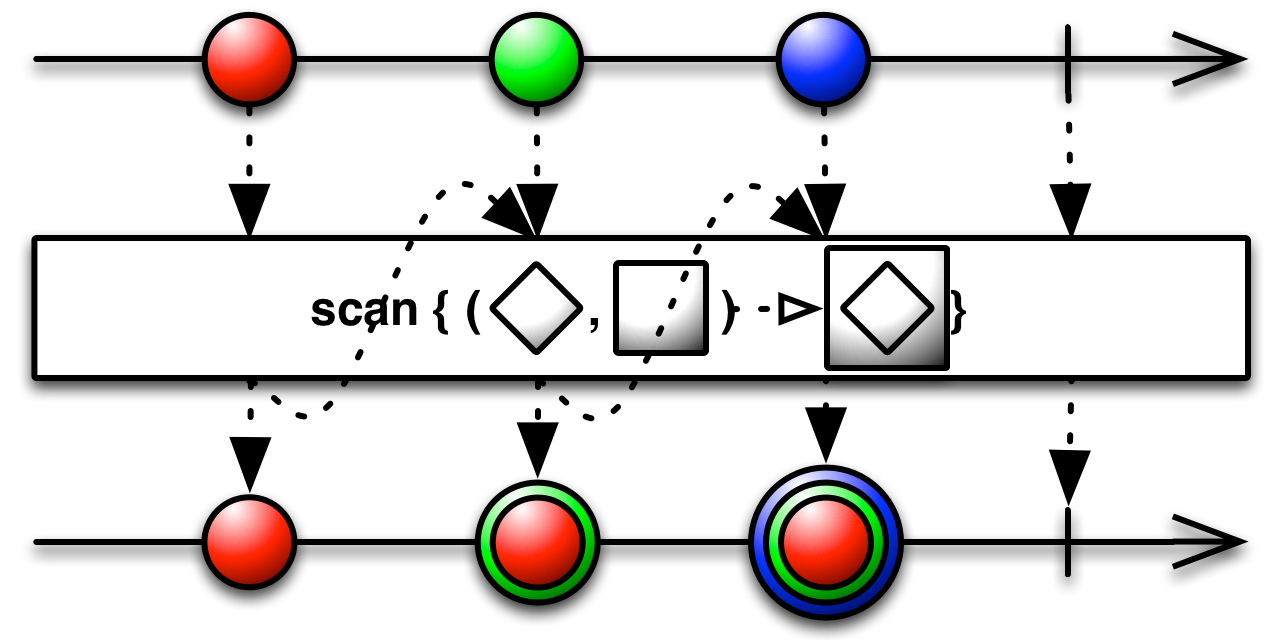
Scan
Apply a function to each item emitted by an Observable, sequentially, and emit each successive value. The Scan operator applies a function to the first item emitted by the source Observable and then emits the result of that function as its own first emission. It also feeds the result of the function back into the function along with the second item emitted by the source Observable in order to generate its second emission. It continues to feed back its own subsequent emissions along with the subsequent emissions from the source Observable in order to create the rest of its sequence.
This sort of operator is sometimes called an “accumulator” in other contexts.
fun scan() {
Observable.range(1, 5)
.scan { sum, item -> sum + item }
.subscribe { items -> println("Next item = $items") }
}
Output:
Next item = 1
Next item = 3
Next item = 6
Next item = 10
Next item = 15
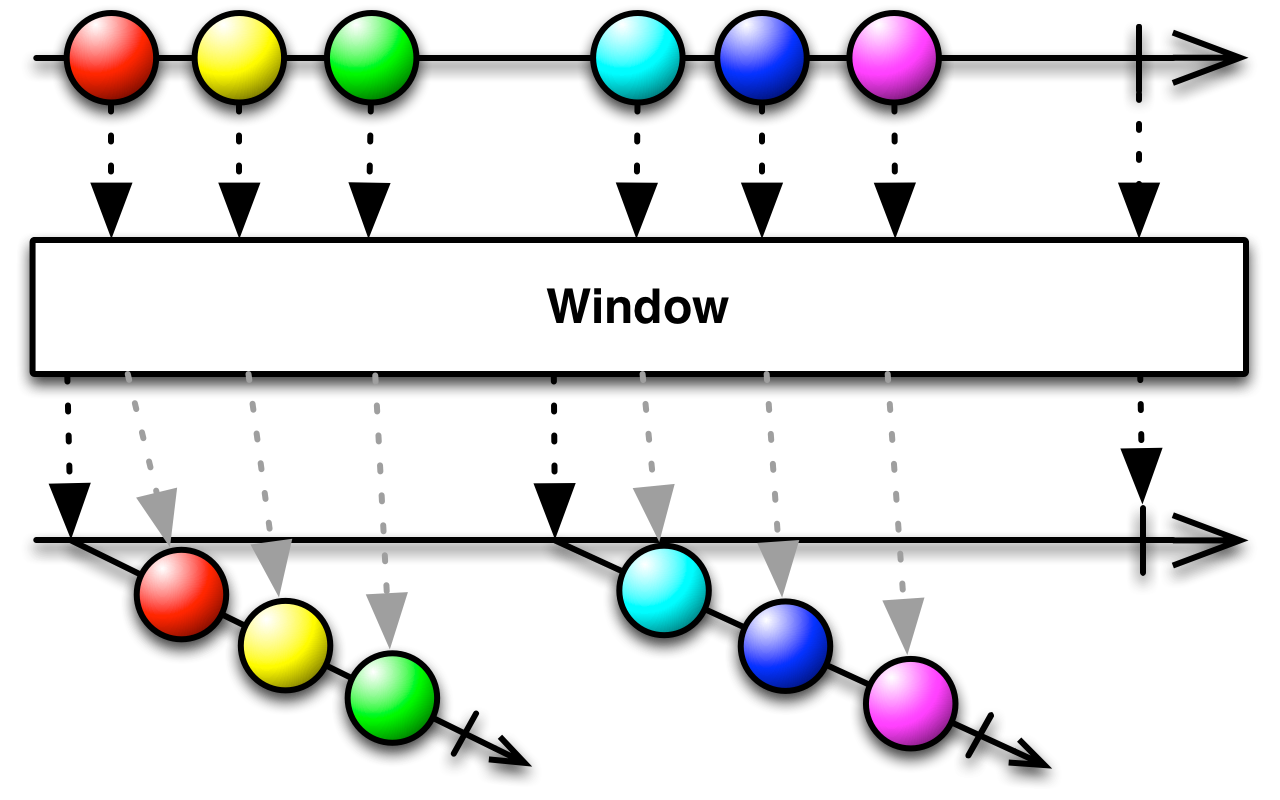
Window
Periodically subdivide items from an Observable into Observable windows and emit these windows rather than emitting the items one at a time. Window is similar to Buffer, but rather than emitting packets of items from the source Observable, it emits Observables, each one of which emits a subset of items from the source Observable and then terminates with an onCompleted notification.
fun window() {
Observable.just(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8)
.window(2)
.subscribe(
{
item ->
println("onNext()")
item.subscribe { innerItem -> println("Next item = $innerItem") }
},
{
println("onError()")
},
{
println("onComplete()")
}
)
}
Output:
onNext()
Next item = 1
Next item = 2
onNext()
Next item = 3
Next item = 4
onNext()
Next item = 5
Next item = 6
onNext()
Next item = 7
Next item = 8
Links
http://reactivex.io/documentation/operators.html
http://reactivex.io/documentation/operators/buffer.html
http://reactivex.io/documentation/operators/flatmap.html
http://reactivex.io/documentation/operators/groupby.html
http://reactivex.io/documentation/operators/map.html
http://reactivex.io/documentation/operators/scan.html
http://reactivex.io/documentation/operators/window.html
 Rx - math_concat
Rx - math_concat