Room
The Room persistence library provides an abstraction layer over SQLite to allow for more robust database access while harnessing the full power of SQLite.
The library helps you create a cache of your app’s data on a device that’s running your app. This cache, which serves as your app’s single source of truth, allows users to view a consistent copy of key information within your app, regardless of whether users have an internet connection.
To use Room in your app, add the following dependencies to your app’s build.gradle file:
dependencies {
def room_version = "2.2.5"
implementation "androidx.room:room-runtime:$room_version"
annotationProcessor "androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version" // For Kotlin use kapt instead of annotationProcessor
// optional - Kotlin Extensions and Coroutines support for Room
implementation "androidx.room:room-ktx:$room_version"
// optional - RxJava support for Room
implementation "androidx.room:room-rxjava2:$room_version"
// optional - Guava support for Room, including Optional and ListenableFuture
implementation "androidx.room:room-guava:$room_version"
// Test helpers
testImplementation "androidx.room:room-testing:$room_version"
}
Components of Room DB
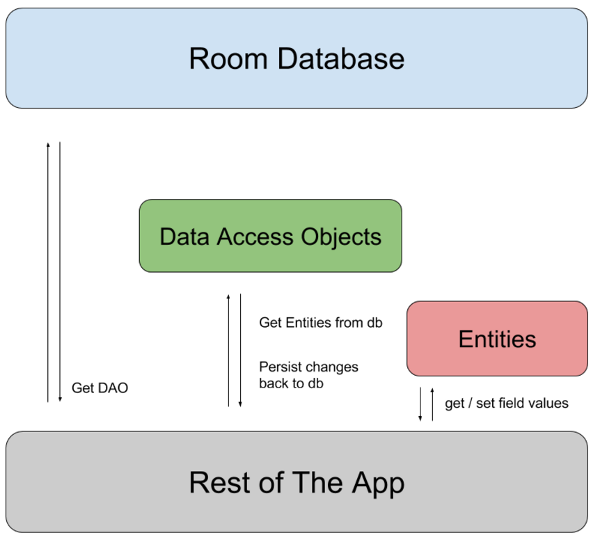
The three major components of Room are:
- Database: It represents the DB, it is an object that holds a connection to the SQLite DB and all the operations are executed through it. It is annotated with
@Database. - Entity: Represents a table within the Room Database. It should be annotated with
@Entity. - DAO: An interface that contains the methods to access the Database. It is annotated with
@Dao.
Sample implementation
This section presents an example implementation of a Room database with a single data entity and a single DAO.
Data entity
The following code defines a User data entity. Each instance of User represents a row in a user table in the app’s database.
@Entity
data class User(
@PrimaryKey val uid: Int,
@ColumnInfo(name = "first_name") val firstName: String?,
@ColumnInfo(name = "last_name") val lastName: String?
)
Data access object (DAO)
The following code defines a DAO called UserDao. UserDao provides the methods that the rest of the app uses to interact with data in the user table.
@Dao
interface UserDao {
@Query("SELECT * FROM user")
fun getAll(): List<User>
@Query("SELECT * FROM user WHERE uid IN (:userIds)")
fun loadAllByIds(userIds: IntArray): List<User>
@Query("SELECT * FROM user WHERE first_name LIKE :first AND " +
"last_name LIKE :last LIMIT 1")
fun findByName(first: String, last: String): User
@Insert
fun insertAll(vararg users: User)
@Delete
fun delete(user: User)
}
Database
The following code defines an AppDatabase class to hold the database. AppDatabase defines the database configuration and serves as the app’s main access point to the persisted data. The database class must satisfy the following conditions:
- The class must be annotated with a
@Databaseannotation that includes anentitiesarray that lists all of the data entities associated with the database; - The class must be an abstract class that extends
RoomDatabase; - For each DAO class that is associated with the database, the database class must define an abstract method that has zero arguments and returns an instance of the DAO class.
@Database(entities = arrayOf(User::class), version = 1)
abstract class AppDatabase : RoomDatabase() {
abstract fun userDao(): UserDao
}
Usage
After you have defined the data entity, the DAO, and the database object, you can use the following code to create an instance of the database:
val db = Room.databaseBuilder(
applicationContext,
AppDatabase::class.java, "database-name"
).build()
You can then use the abstract methods from the AppDatabase to get an instance of the DAO. In turn, you can use the methods from the DAO instance to interact with the database:
val userDao = db.userDao()
val users: List<User> = userDao.getAll()
Configuring Compiler Options
Room has the following annotation processor options:
room.schemaLocation: Configures and enables exporting database schemas into JSON files in the given directory.room.incremental: Enables Gradle incremental annotation proccesor.room.expandProjection: Configures Room to rewrite queries such that their top star projection is expanded to only contain the columns defined in the DAO method return type.
Links
Save data in a local database using Room
| [Using Room Database | Android Jetpack](https://medium.com/mindorks/using-room-database-android-jetpack-675a89a0e942) |
Room — Kotlin, Android Architecture Components
Further reading
Accessing data using Room DAOs
Defining data using Room entities
 Android - no_image
Android - no_image