AndroidManifest
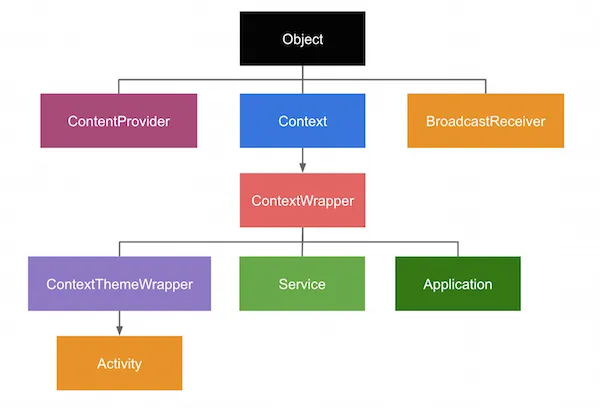
The AndroidManifest.xml file contains information of your package, including components of the application such as activities, services, broadcast receivers, content providers etc.
Responsibilities
- Protect the application to access any protected parts by providing the permissions.
- Declares the android api that the application is going to use.
- Declares lists the instrumentation classes. The instrumentation classes provides profiling and other informations.
- Specify whether app should be install on an SD card of the internal memory.
Nodes
-
uses-sdk - It is used to define a minimum and maximum SDK version that must be available on a device so that our application function properly. However, beware that attributes in the **
** element are overridden by corresponding properties in the `build.gradle` -
uses-configuration - The uses-configuration nodes are used to specify the combination of input mechanisms that are supported by our application.
-
uses-features - It is used to specify which hardware and software features your app needs.
-
supports-screens - It is used to describe the screen support for application.
-
permission - It is used to create permissions to restrict access to shared application components. Also used the existing platform permissions for this purpose or define your own permissions in the manifest.
-
application - The declaration of the application. This element contains subelements that declare each of the application’s components (such as Activity, Service, Content Provider, and Broadcast Receiver) and has attributes that can affect all the components.
Links
https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/manifest/manifest-intro
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/application-manifest-file-android/

 Android - anr_example_framed
Android - anr_example_framed