Design Consistent Hashing
For horizontal scaling, it is important to distribute requests across servers efficiently.
Consistent hashing is a common approach to achieve this.
The rehashing problem
One way to determine which server a request gets routed to is by applying a simple hash+module formula:
serverIndex = hash(key) % N, where N is the number of servers
This makes it so requests are distributed uniformly across all servers. However, whenever new servers are added or removed, the result of the above equation is very different, meaning that a lot of requests will get rerouted across servers.
This causes a lot of cache misses as clients will be connected to new instances which will have to fetch the user data from cache all over again.
Consistent hashing
Consistent hashing is a technique which allows only a K/N servers to be remapped whenever N changes, where K is the number of keys.
For example, K=100, N=10 -> 10 re-mappings, compared to close to 100 in the normal scenario.
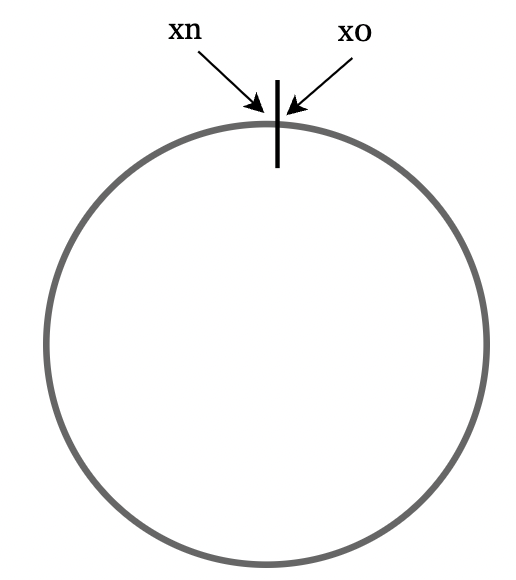
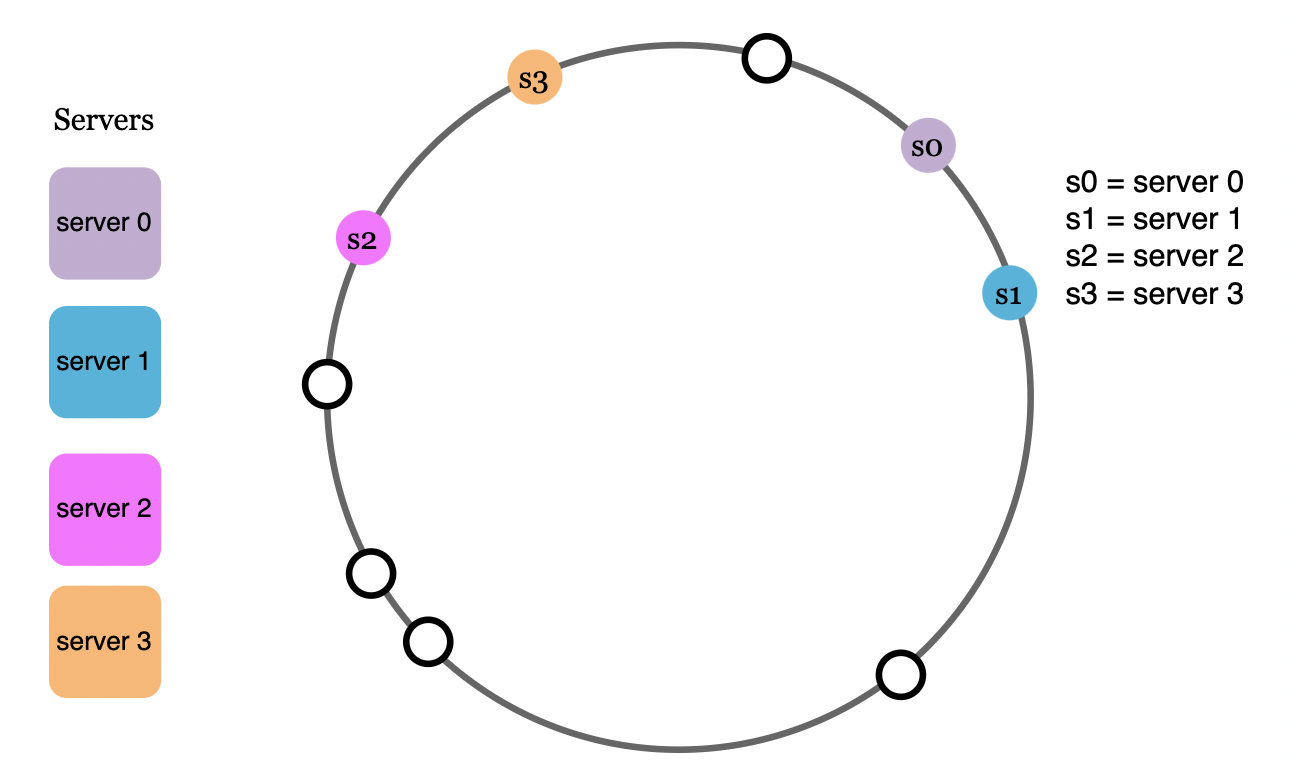
Hash space and hash ring
A hash ring is a visualization of the possible key space of a given hash algorithm, which is combined into a ring-like structure:
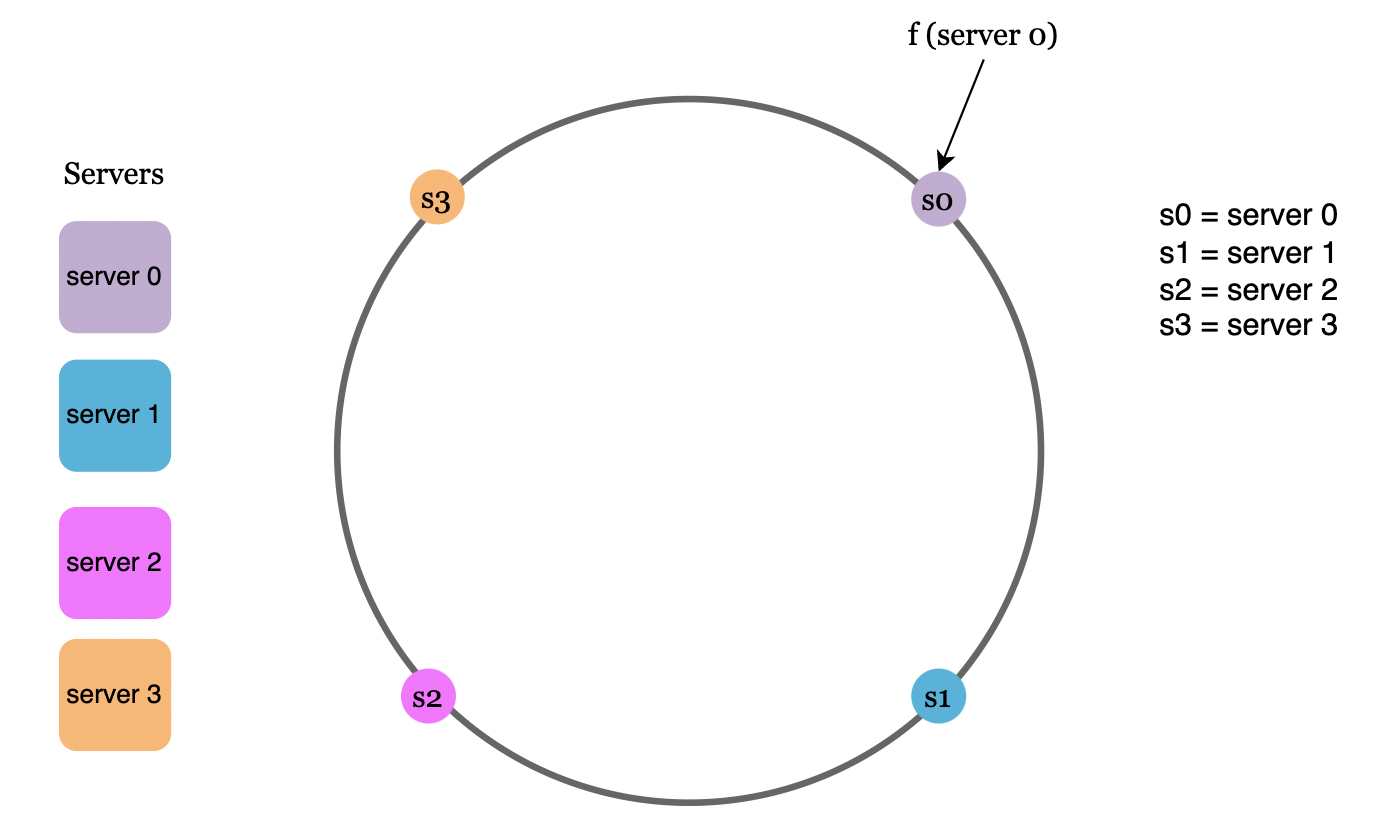
Hash servers
Using the same hash function for the requests, we map the servers based on server IP or name onto the hash ring:
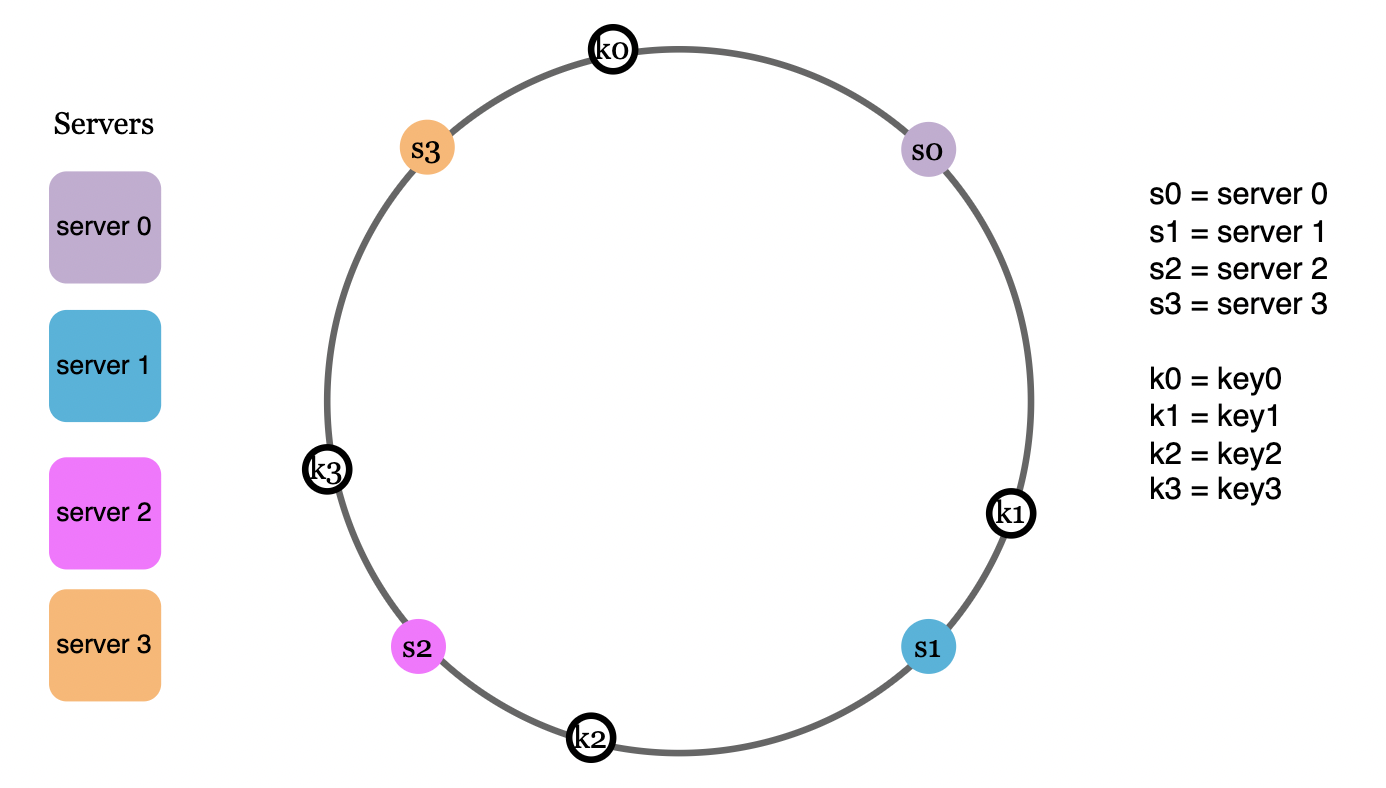
Hash keys
The hashes of the requests also get resolved somewhere along the hash ring. Notice that we’re not using the modulo operator in this case:
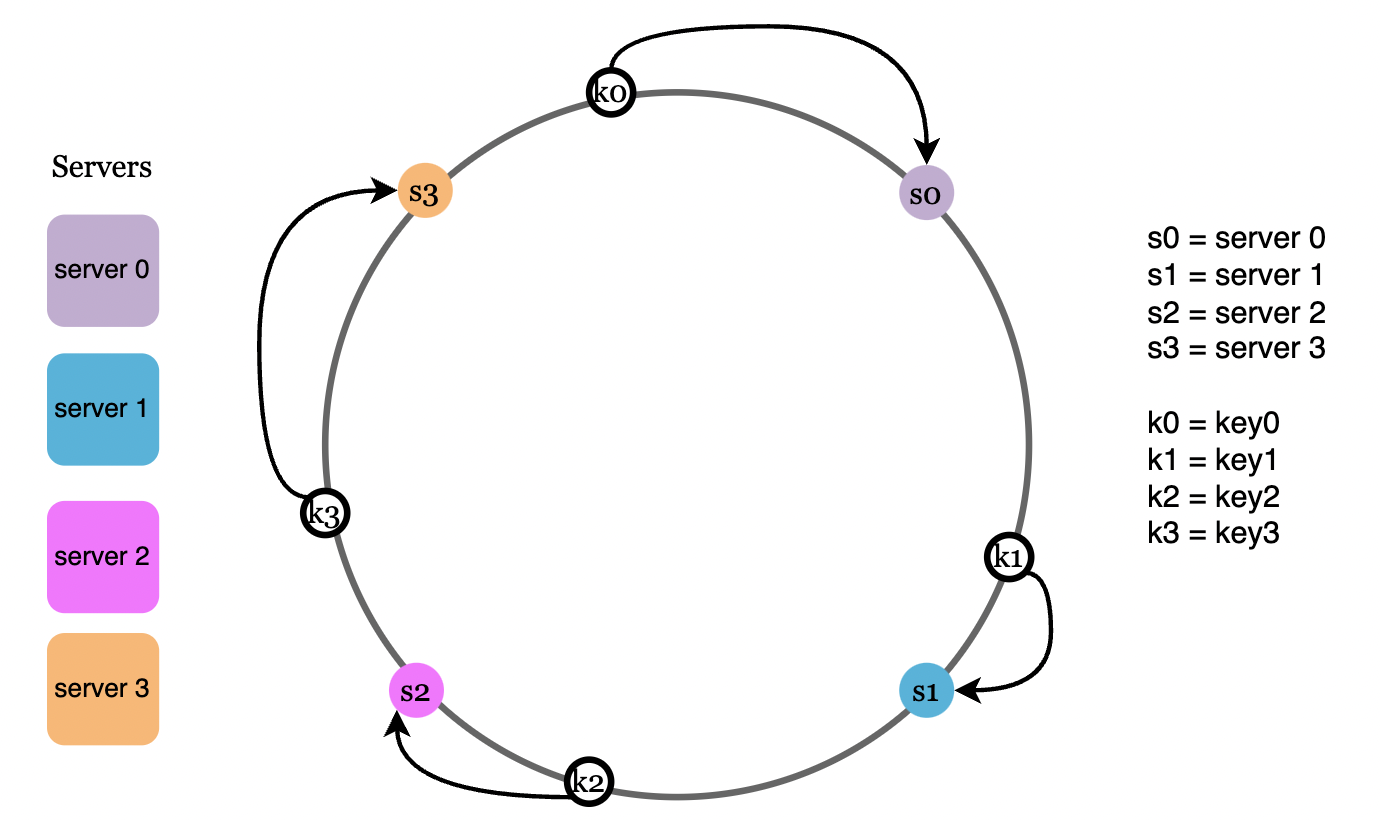
Server lookup
Now, to determine which server is going to serve each request, we go clockwise from the request’s hash until we reach the first server hash:
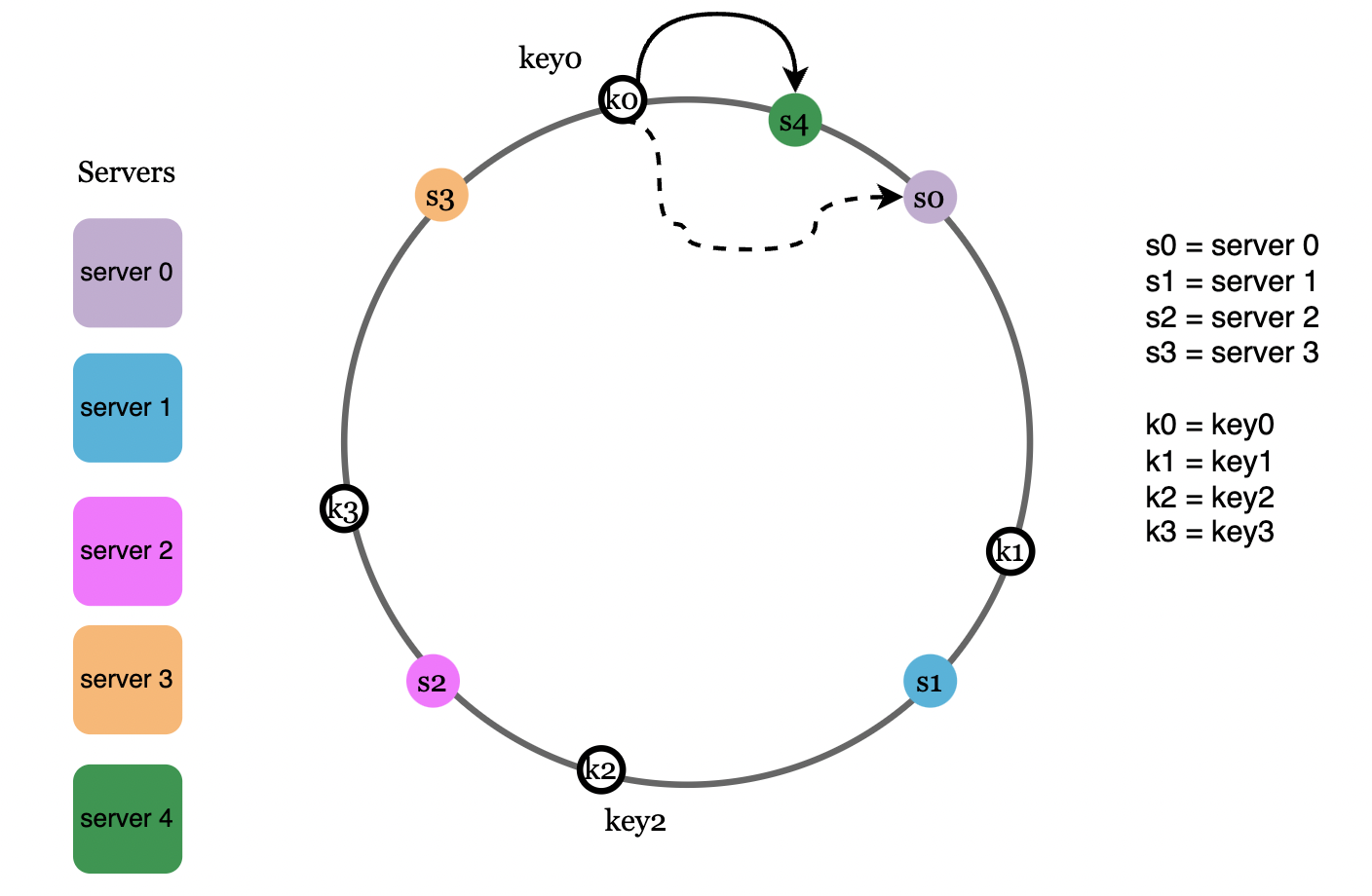
Add a server
Via this approach, adding a new server causes only one of the requests to get remapped to a new server:
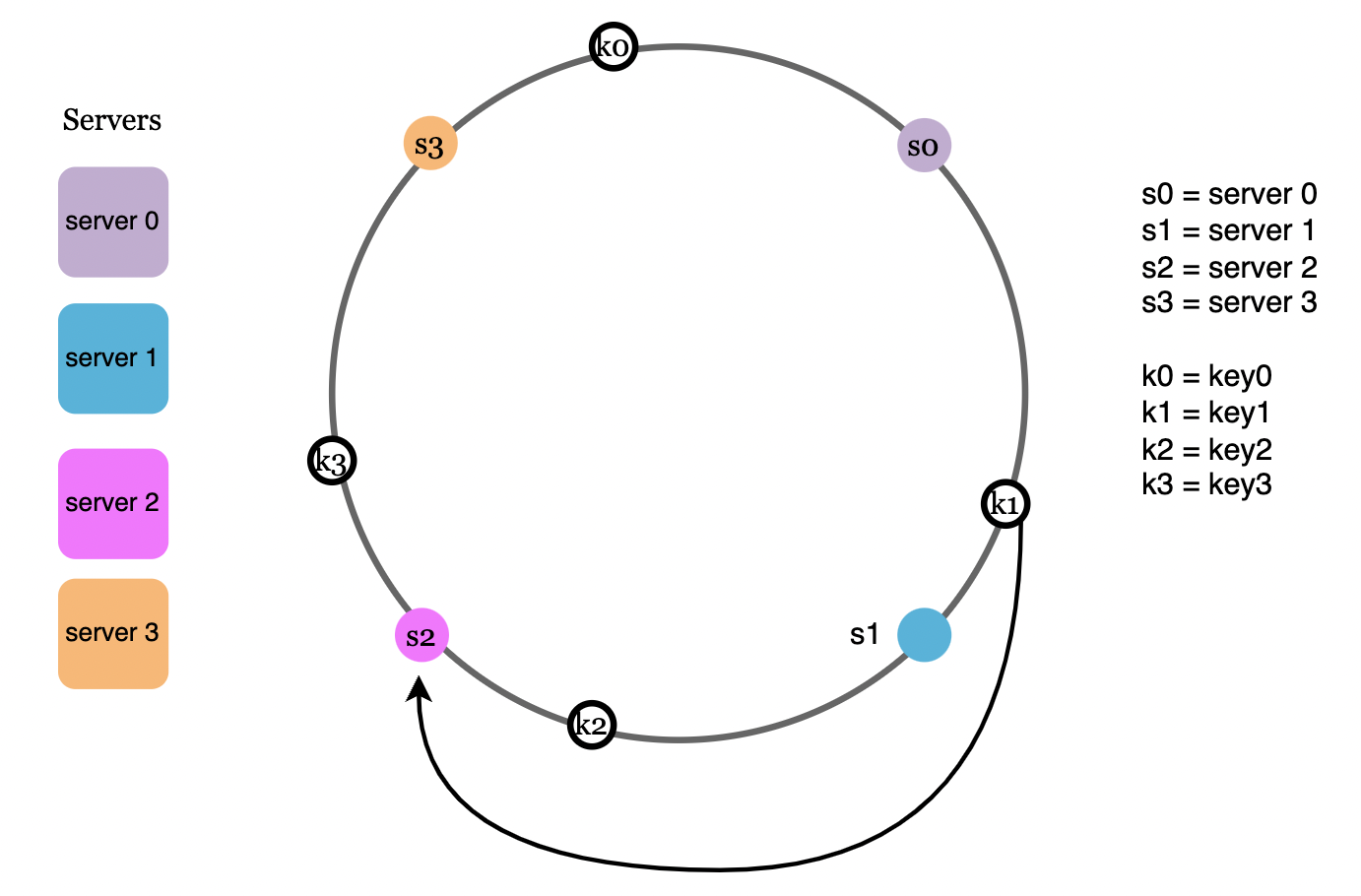
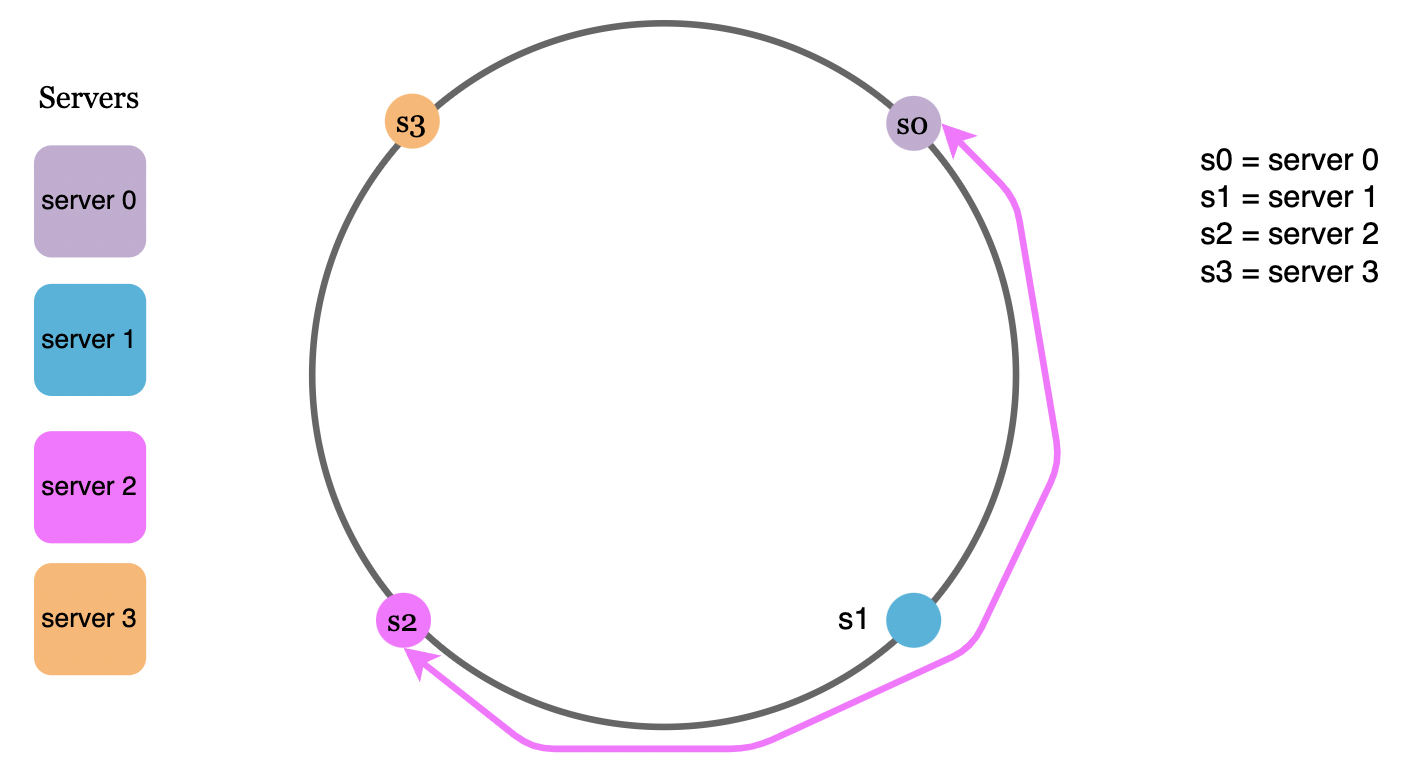
Remove a server
Likewise, removing a server causes only a single request to get remapped:
Two issues in the basic approach
The first problem with this approach is that hash partitions can be uneven across servers:
The second problem derives from the first - it is possible that requests are unevenly distributed across servers:
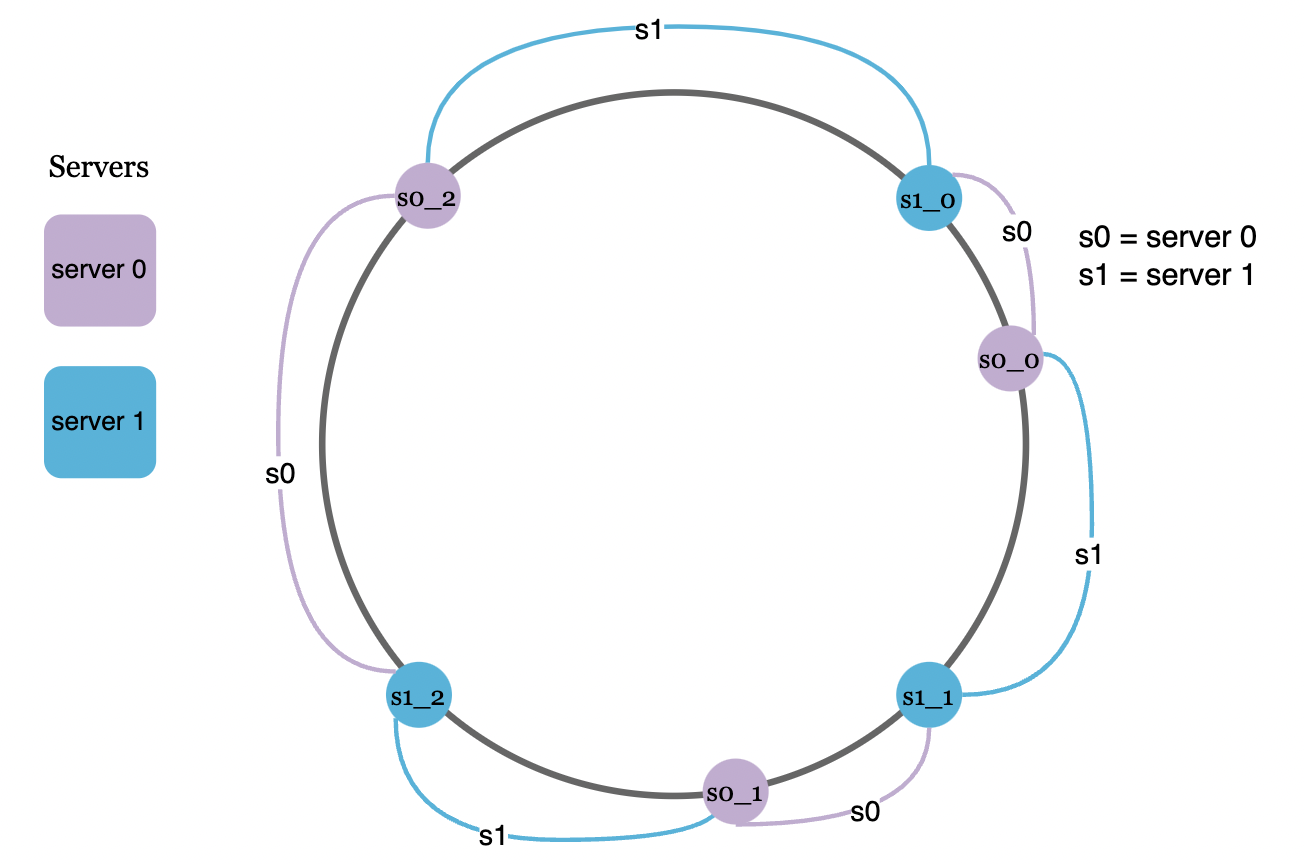
Virtual nodes
To solve this issue, we can map a servers on the hash ring multiple times, creating virtual nodes and assigning multiple partitions to the same server:
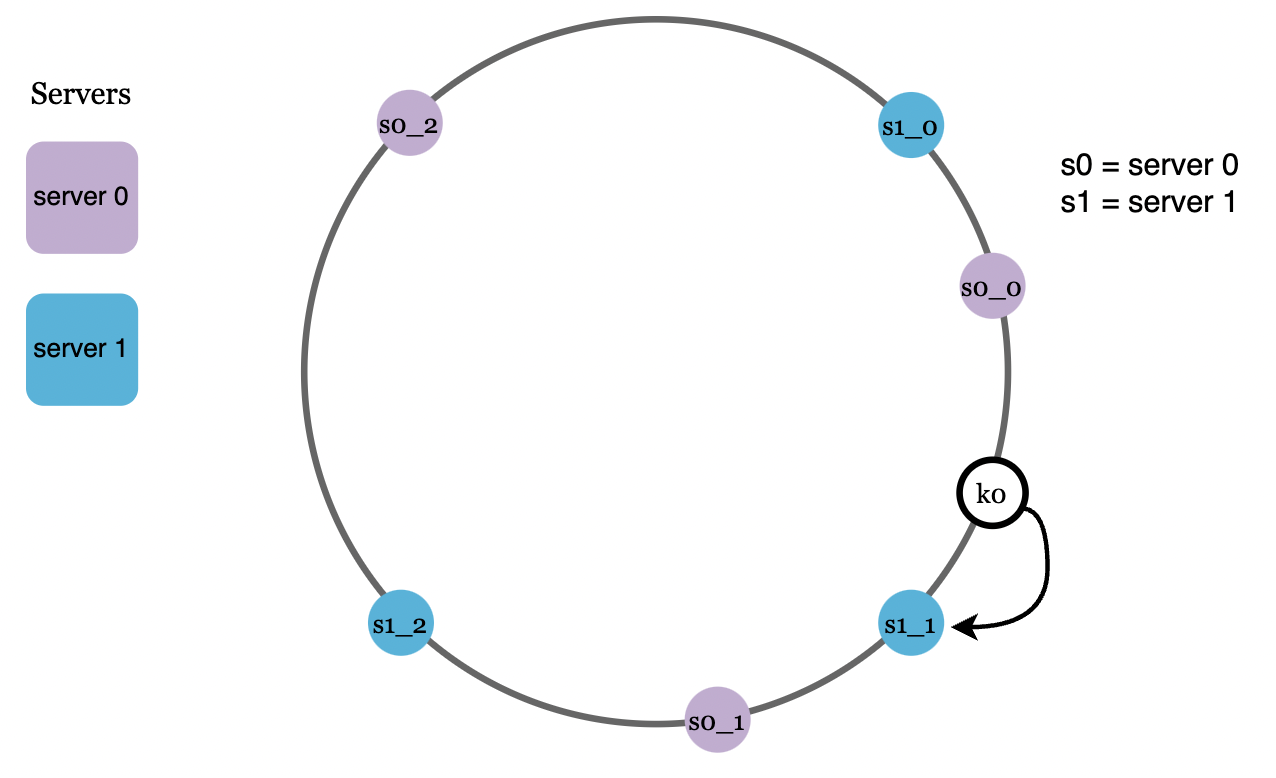
Now, a request is mapped to the closest virtual node on the hash ring:
The more virtual nodes we have, the more evenly distributed the requests will be.
An experiment showed that between 100-200 virtual nodes leads to a standard deviation between 5-10%.
Wrap up
Benefits of consistent hashing:
- Very low number of keys are distributed in a re-balancing event
- Easy to scale horizontally as data is uniformly distributed
- Hotspot issue is mitigated by uniformly distributing data, related to eg a celebrity, which is often accessed
Examples of real-world applications of consistent hashing:
- Amazon’s DynamoDB partitioning component
- Data partitioning in Cassandra
- Discord chat application
- Akamai CDN
- Maglev network load balancer
 Chapter05 - server-side-rate-limiter
Chapter05 - server-side-rate-limiter