Deque interface
public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E>
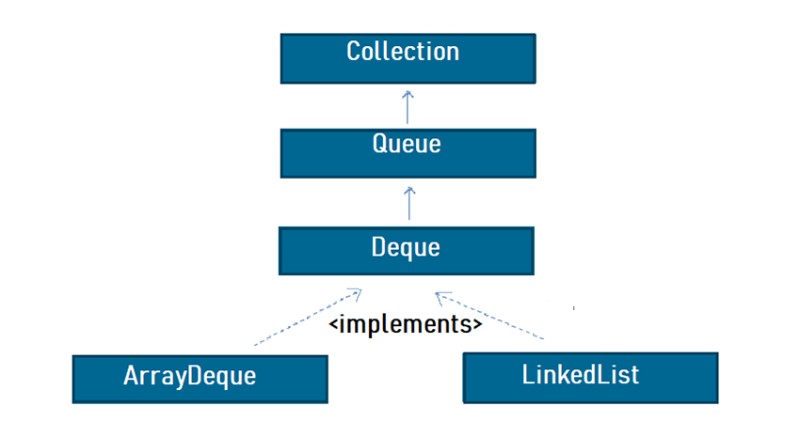
A linear collection that supports element insertion and removal at both ends. The name deque is short for “double ended queue” and is usually pronounced “deck”. Most Deque implementations place no fixed limits on the number of elements they may contain, but this interface supports capacity-restricted deques as well as those with no fixed size limit.
This interface defines methods to access the elements at both ends of the deque. Methods are provided to insert, remove, and examine the element. Each of these methods exists in two forms: one throws an exception if the operation fails, the other returns a special value (either null or false, depending on the operation). The latter form of the insert operation is designed specifically for use with capacity-restricted Deque implementations; in most implementations, insert operations cannot fail.
The twelve methods described above are summarized in the following table:
| First Element (Head) | Last Element (Tail) | |||
| Throws exception | Special value | Throws exception | Special value | |
| Insert | addFirst(e) |
offerFirst(e) |
addLast(e) |
offerLast(e) |
| Remove | removeFirst() |
pollFirst() |
removeLast() |
pollLast() |
| Examineb> | getFirst() |
peekFirst() |
getLast() |
peekLast() |
This interface extends the Queue interface. When a deque is used as a queue, FIFO (First-In-First-Out) behavior results. Elements are added at the end of the deque and removed from the beginning. The methods inherited from the Queue interface are precisely equivalent to Deque methods as indicated in the following table:
| Queue Method | Equivalent Deque Method |
|---|---|
add(e) |
addLast(e) |
offer(e) |
offerLast(e) |
remove() |
removeFirst() |
poll() |
pollFirst() |
element() |
getFirst() |
peek() |
peekFirst() |
Deques can also be used as LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) stacks. This interface should be used in preference to the legacy Stack class. When a deque is used as a stack, elements are pushed and popped from the beginning of the deque. Stack methods are precisely equivalent to Deque methods as indicated in the table below:
| Stack Method | Equivalent Deque Method |
|---|---|
push(e) |
addFirst(e) |
pop() |
removeFirst() |
peek() |
peekFirst() |
poll() |
pollFirst() |
element() |
getFirst() |
peek() |
peekFirst() |
Note that the peek method works equally well when a deque is used as a queue or a stack; in either case, elements are drawn from the beginning of the deque.
Unlike the List interface, this interface does not provide support for indexed access to elements.
While Deque implementations are not strictly required to prohibit the insertion of null elements, they are strongly encouraged to do so. Users of any Deque implementations that do allow null elements are strongly encouraged not to take advantage of the ability to insert nulls. This is so because null is used as a special return value by various methods to indicated that the deque is empty.
Most used Implementing Classes
ArrayDequeResizable-array implementation of theDequeinterface. Array deques have no capacity restrictions; they grow as necessary to support usage. They are not thread-safe; in the absence of external synchronization, they do not support concurrent access by multiple threads. Null elements are prohibited. This class is likely to be faster thanStackwhen used as a stack, and faster thanLinkedListwhen used as a queue. 1LinkedList: Doubly-linked list implementation of theListandDequeinterfaces. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all elements (includingnull). All of the operations perform as could be expected for a doubly-linked list. Operations that index into the list will traverse the list from the beginning or the end, whichever is closer to the specified index. 2
Links
Next Questions
Describe Queue interface from java collection
What do you know about LinkedList?
Further reading
Deque interface in Java with Example
 Java - no_image
Java - no_image