Queue interface
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E>
A collection designed for holding elements prior to processing. Besides basic Collection operations, queues provide additional insertion, extraction, and inspection operations. Each of these methods exists in two forms: one throws an exception if the operation fails, the other returns a special value (either null or false, depending on the operation). The latter form of the insert operation is designed specifically for use with capacity-restricted Queue implementations; in most implementations, insert operations cannot fail.
| Concurrency | Throws exception | Returns special value |
|---|---|---|
| Insert | add(e) |
offer(e) |
| Remove | remove() |
poll() |
| Examine | element() |
peek() |
Queues typically, but do not necessarily, order elements in a FIFO (first-in-first-out) manner. Among the exceptions are priority queues, which order elements according to a supplied comparator, or the elements’ natural ordering, and LIFO queues (or stacks) which order the elements LIFO (last-in-first-out). Whatever the ordering used, the head of the queue is that element which would be removed by a call to remove() or poll(). In a FIFO queue, all new elements are inserted at the tail of the queue. Other kinds of queues may use different placement rules. Every Queue implementation must specify its ordering properties.1
The Queue interface does not define the blocking queue methods, which are common in concurrent programming. These methods, which wait for elements to appear or for space to become available, are defined in the BlockingQueue interface, which extends this interface.
Queue implementations generally do not allow insertion of null elements, although some implementations, such as LinkedList, do not prohibit insertion of null. Even in the implementations that permit it, null should not be inserted into a Queue, as null is also used as a special return value by the poll method to indicate that the queue contains no elements.
Queue implementations generally do not define element-based versions of methods equals and hashCode but instead inherit the identity based versions from class Object, because element-based equality is not always well-defined for queues with the same elements but different ordering properties.2
Most used Implementing Classes
PriorityQueue: An unbounded priority queue based on a priority heap. The elements of the priority queue are ordered according to their natural ordering, or by aComparatorprovided at queue construction time, depending on which constructor is used. A priority queue does not permitnullelements. A priority queue relying on natural ordering also does not permit insertion of non-comparable objects (doing so may result inClassCastException).3LinkedList: Doubly-linked list implementation of theListandDequeinterfaces. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all elements (includingnull). All of the operations perform as could be expected for a doubly-linked list. Operations that index into the list will traverse the list from the beginning or the end, whichever is closer to the specified index. 4PriorityBlockingQueue: An unbounded blocking queue that uses the same ordering rules as classPriorityQueueand supplies blocking retrieval operations. While this queue is logically unbounded, attempted additions may fail due to resource exhaustion (causingOutOfMemoryError). This class does not permitnullelements. A priority queue relying on natural ordering also does not permit insertion of non-comparable objects (doing so results inClassCastException). 5
Links
Next questions
Describe Deque interface from java collection
What do you know about LinkedList?
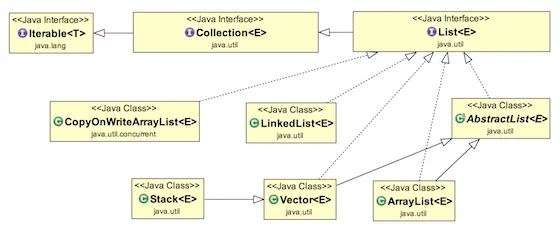 Java - java_list_class_diagram
Java - java_list_class_diagram