Cloneable interface
A class implements the Cloneable interface to indicate to the Object.clone() method that it is legal for that method to make a field-for-field copy of instances of that class. Invoking Object’s clone method on an instance that does not implement the Cloneable interface results in the exception CloneNotSupportedException being thrown. By convention, classes that implement this interface should override Object.clone (which is protected) with a public method. Note that this interface does not contain the clone method. Therefore, it is not possible to clone an object merely by virtue of the fact that it implements this interface. Even if the clone method is invoked reflectively, there is no guarantee that it will succeed.
Advantage of Object cloning:
- You don’t need to write lengthy and repetitive codes. Just use an abstract class with a 4- or 5-line long clone() method.
- It is the easiest and most efficient way for copying objects, especially if we are applying it to an already developed or an old project.
- Clone() is the fastest way to copy array.
Disadvantage of Object cloning:
- To use the
Object.clone()method, we have to change a lot of syntaxes to our code, like implementing aCloneableinterface, defining theclone()method and handlingCloneNotSupportedException, and finally, callingObject.clone()etc. - We have to implement
Cloneableinterface while it doesn’t have any methods in it. We just have to use it to tell the JVM that we can performclone()on our object. Object.clone()doesn’t invoke any constructor so we don’t have any control over object construction.- If you want to write a clone method in a child class then all of its superclasses should define the
clone()method in them or inherit it from another parent class. Otherwise, thesuper.clone()chain will fail. Object.clone()supports only shallow copying but we will need to override it if we need deep cloning.
Example:
public class Student implements Cloneable {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student std1 = new Student();
try {
std1.setName("John");
Student std2 = (Student) std1.clone();
System.out.println(std1.getName());
System.out.println(std2.getName());
std2.setName("Mike");
System.out.println(std1.getName());
System.out.println(std2.getName());
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Links
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/Cloneable.html
https://www.javatpoint.com/object-cloning
https://beginnersbook.com/2015/01/cloneable-interface-in-java-object-cloning/

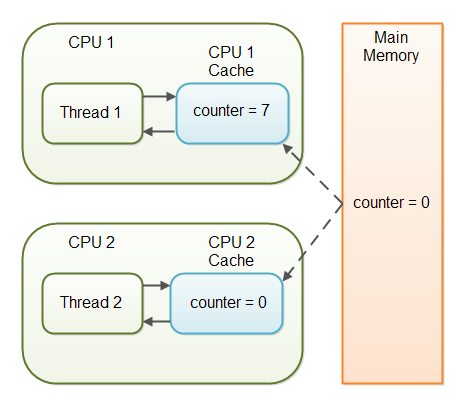 Java - volatile
Java - volatile