Iterator interface
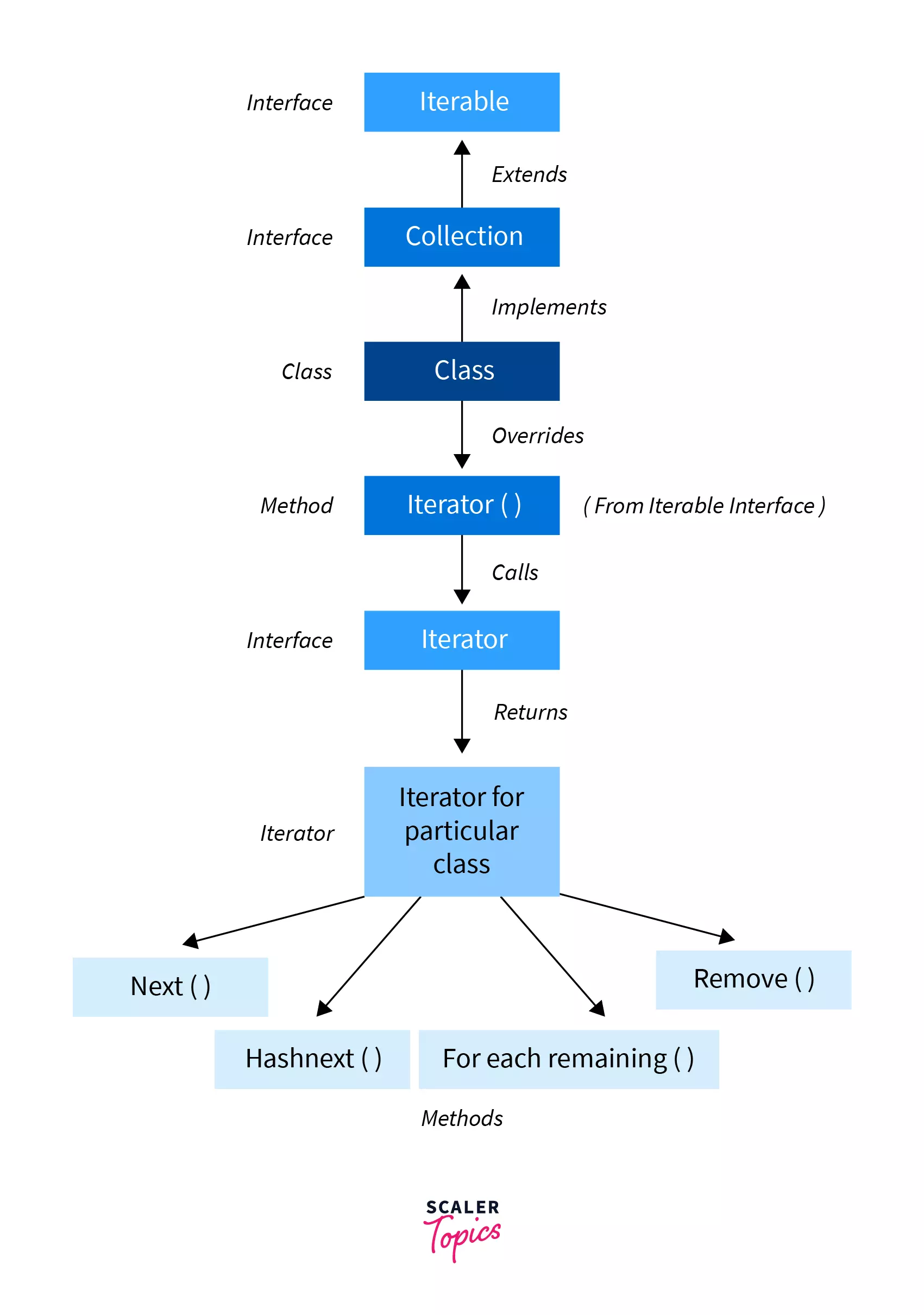
In Java, an Iterator is one of the Java cursors. Java Iterator is an interface that is practiced in order to iterate over a collection of Java object components entirety one by one. It belongs to java.util package. 1
The Java Iterator is also known as the universal cursor of Java as it is appropriate for all the classes of the Collection framework. The Java Iterator also helps in the operations like READ and REMOVE. 2
Methods of Iterator
The Iterator interface provides 4 methods that can be used to perform various operations on elements of collections:
hasNext()- returnstrueif there exists an element in the collection;next()- returns the next element of the collection;remove()- removes the last element returned by thenext();forEachRemaining()- performs the specified action for each remaining element of the collection.
Example: Implementation of Iterator
In the example below, we have implemented the hasNext(), next(), remove() and forEachRemining() methods of the terator interface in an array list.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an ArrayList
ArrayList<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>();
numbers.add(1);
numbers.add(3);
numbers.add(2);
System.out.println("ArrayList: " + numbers);
// Creating an instance of Iterator
Iterator<Integer> iterate = numbers.iterator();
// Using the next() method
int number = iterate.next();
System.out.println("Accessed Element: " + number);
// Using the remove() method
iterate.remove();
System.out.println("Removed Element: " + number);
System.out.print("Updated ArrayList: ");
// Using the hasNext() method
while(iterate.hasNext()) {
// Using the forEachRemaining() method
iterate.forEachRemaining((value) -> System.out.print(value + ", "));
}
}
}
Output:
ArrayList: [1, 3, 2]
Acessed Element: 1
Removed Element: 1
Updated ArrayList: 3, 2,
Advantage of Iterator in Java
- An iterator can be used with any collection classes;
- We can perform both read and remove operations;
- It acts as a universal cursor for collection API.
Limitation of Iterator in Java
- We can perform either read operation or remove operation;
- We cannot perform the replacement of new objects.
Links
[Iterator in Java |
Methods, Example](https://www.scientecheasy.com/2020/09/java-iterator.html/) |
Next questions
What is the difference between a Stream and an Iterator?
Further Reading
Java Iterable Interface: Iterator, ListIterator, and Spliterator
 Java - no_image
Java - no_image